A “blood draw” is a method of collecting a hematologic sample from one of your peripheral veins which can then be sent to a laboratory for further analysis as needed.
An electrocardiogram, also known as an EKG or ECG, is a testing method that evaluates the electrical activity of your heart. An EKG translates the heart’s electrical activity into line tracings on paper so that they can be analyzed.
ERG (electroretinography) and EOG (electrooculography) measure the electrical response of the different layers and components of the retina to light and dark stimuli. These tests are usually very useful in the diagnosis of hereditary conditions affecting the retina such as retinitis pigmentosa or Stargardt’s disease.
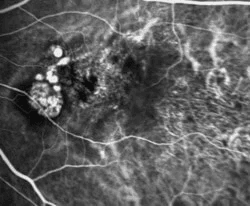
Fluorescein Angiography is a photographic study of the blood supply to the retina. Fluorescein dye is injected into the vein of an arm and this yellow dye passes through the blood vessels in your retina. A specialized camera is then used to take digital photographs of the blood vessels. This procedure is used to diagnose many different disorders affecting the retina and is generally very safe. The dye can be used in people who are allergic to shellfish or iodine and can also be used in patients who previously had reactions to contrast dye during radiologic procedures. However, in some rare instances, the dye may cause an allergic reaction and this will be closely monitored during the procedure. Patients who undergo fluorescein angiography may also notice the urine is yellow or green on the day of the procedure. This is normal and should stop within a day or two.
Fundus Autofluorescence utilizes a blue-green wavelength light to visualize conditions that affect the pigment layer of the retina (retinal pigment epithelium). This simple non-invasive technique has greatly expanded our understanding and management of many different diseases affecting the macula, including dry age-related macular degeneration. Fundus autofluorescence takes only a few minutes and has no known adverse effects.
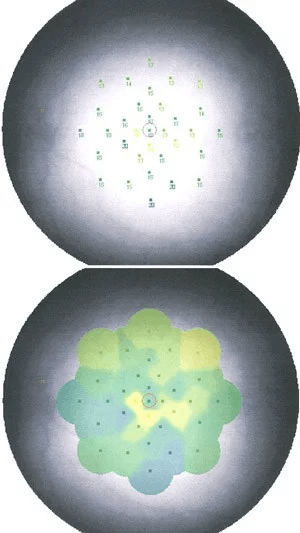
Certain eye diseases, such as glaucoma and retinitis pigmentosa may cause loss of peripheral vision over time. This loss of peripheral vision can be documented and followed using visual field testing. Depending on the patient’s vision and the degree of the visual field loss, your doctor may recommend a Humphrey or a Goldmann visual field test.
During an automated Humphrey visual field test, a patient is asked to look at a target straight ahead and then press a button if and when they see a light that shows up in their peripheral visual field. A Goldmann visual field is less commonly performed. It is generally used in patients who have very poor vision or advanced visual field loss. In a Goldmann visual field test, an examiner manually moves a light target of differing sizes and intensities while the patient looks straight ahead. The patient lets the technician know as soon as they see the target in their visual field. In a Humphrey test the computer automatically generates and prints out a copy of the patient’s visual field test. In a Goldmann test the examiner draws or maps out the visual field as they are performing the test.
Microperimetry allows us to measure the visual function of a specific part of the retina. Usually the test is used to measure macular function. Before the test begins the patient stays in a dimly lit room for a few minutes. After this, the patient is asked to fixate on a target and is presented lights of varying intensity. The patient presses a button every time they see a light stimulus. The computer generates a map of the specific part of the retina that was tested, measuring the visual function of the areas tested. The microperimeter can be correlated with optical coherence tomography and is used to objectively measure the visual function of a particular area of the retina over time.
Visual acuity is the most important tool used to assess your visual function. Refraction with ETDRS BCVA is used to determine your precise visual acuity at study visits. To do this, you will sit in a specific chair wearing trial frames over your eyes (these frames look like glasses). You will look through the frames and focus on an eye chart exactly 20 feet in the distance. We will insert different lenses of different strengths into the frames to assess your best possible visual acuity. We will ask you if the chart appears more or less clear when different lenses are in place. The test is performed one eye at a time.

OCT is an imaging technique that utilizes light wave interferometry to produce high resolution cross-sectional images, similar to a computed tomography (CT) scan of the retina. The images measure the thickness of the retina and are very useful in the diagnosis and follow-up of many diseases affecting the macula. The scan takes only a few minutes and is non-invasive with no adverse effects. High resolution Spectral Domain OCT testing is available at all of our offices.
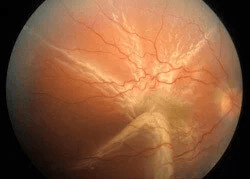
Classic retinal photography and angiography usually covers only about 45 degrees, or roughly 20% of the retina at one time. Many abnormalities of the peripheral retina are difficult to image during fluorescein angiography and therefore we are unable to evaluate it thoroughly. However, with ultra-widefield photography we are able to view a much larger portion of the retina in one image.
Ultra-widefield imaging enables us to view almost 200 degrees or 80% of the retina at one time. Fluorescein angiography can also be done using ultra-widefield photography and it provides superior visibility of the peripheral retina. Many abnormalities in the peripheral retina that were previously unable to be viewed on traditional angiography are demonstrated clearly on wide-field imaging. However it is important to note that ultra-widefield photography, or any photography for that matter, does not take the place of a good, dilated eye exam by your doctor.
Most of our offices are equipped with instruments that allow ultra-widefield photography and fluorescein angiography.
Vital signs are specific measurements obtained in order to assess some of the most basic functions of your body such as your body temperature, pulse rate, blood pressure and respiratory rate. These are measured efficiently and without invasive testing.

